个人简介 学术任职 学术论著 专家风采
个人简介
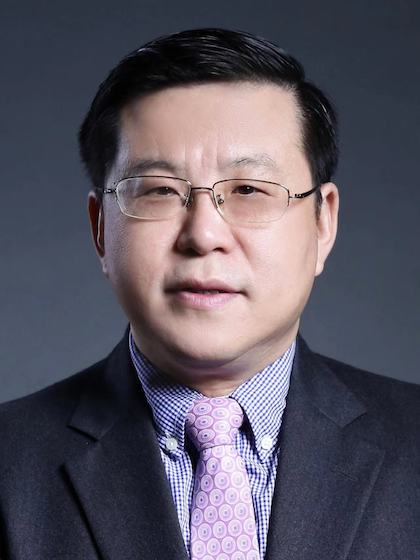
龚侃,北京大学第一医院泌尿外科教授、主任医师、博士生导师、博士后合作导师,担任北京大学泌尿外科研究所副所长,北京大学第一医院肿瘤转化中心副主任,北京大学第一医院科研处处长。长期致力于泌尿生殖系统肿瘤的罕见疑难病的诊、防、治攻关研究,主持科技部重大项目课题、国自然重点专项和面上基金、北京市自然科学基金等20余项。在Cancer Discovery、PNAS、Cancer Research等权威杂志发表SCI论文100余篇,授权发明专利3项,其中1项成功转化成产品上市。牵头多部专家共识和指南并在全国推广,主编国际首部遗传性肾癌专著。荣获中华医学科技奖、教育部科技进步奖、华夏科技进步奖等多个奖项。
学术任职
现为“国家高层次人才特殊支持计划(中组部万人计划)”、科技部“中青年科技创新领军人才”、教育部“新世纪优秀人才”、中华医学会罕见病分会第一届委员会委员、中华医学会泌尿外科罕见疑难疾病联盟主席、中华医学会泌尿外科分会肿瘤学组委员、中华医学会泌尿外科分会转化学组副组长、中国医促会泌尿外科分会副主任委员、中国医师协会泌尿外科肿瘤委员会委员、中国研究型医院学会罕见病分会常务理事、国际 VHL 联盟咨询委员(中国唯一)、《中国泌尿外科疾病诊断治疗指南——前列腺癌》编委。
学术论著
1. Xie, H., Zhou, J., Liu, X., Xu, Y., Hepperla, J. A., ... & Gong, K.*, Zhang, Q.* (2022). USP13 promotes deubiquitination of ZHX2 and tumorigenesis in kidney cancer. PNAS, 119(36): e2119854119. (IF=11.1)
2. Zhou, J., & Gong, K.* (2022). Belzutifan: a novel therapy for von Hippel–Lindau disease. Nature Reviews Nephrology, 1-2. (IF= 42.439)
3. Hu, L., Xie, H., Liu, X., Potjewyd, F., James, L. I., Wilkerson, E. M., ... & Gong, K.*, Zhang, Q.* (2019). TBK1 is a Synthetic Lethal Target in Cancer with VHL Loss. Cancer Discovery, 10(3): 460-475. (IF= 38.272)
4. Ning, X. H., Zhang, N., Li, T., Wu, P. J., Wang, X., Li, X. Y., ... & Gong, K.* (2014). Telomere shortening is associated with genetic anticipation in Chinese Von Hippel–Lindau disease families. Cancer research, 74(14), 3802-3809. (IF= 13.312)
5. Liu, S. J., Wang, J. Y., Peng, S. H., Li, T., Ning, X. H., Hong, B. A., ... & Gong, K.* (2018). Genotype and phenotype correlation in von Hippel–Lindau disease based on alteration of the HIF-α binding site in VHL protein. Genetics in Medicine, 20(10), 1266. (IF= 8.864)
专家风采
1.2017年 “国家高层次人才特殊支持计划(中组部万人计划)”
2.2016年 科技部“中青年科技创新领军人才”
3.2015年 中华医学科技奖三等奖(第一完成人)
4.2014年 北京大学医学部优秀党员
5.2012年 教育部科技进步二等奖(第一完成人)
6.2011年 华夏科技进步奖二等奖(第一完成人)
7.2010年 教育部“新世纪优秀人才”
现为“国家高层次人才特殊支持计划(中组部万人计划)”、科技部“中青年科技创新领军人才”、教育部“新世纪优秀人才”、中华医学会罕见病分会第一届委员会委员、中华医学会泌尿外科罕见疑难疾病联盟主席、中华医学会泌尿外科分会肿瘤学组委员、中华医学会泌尿外科分会转化学组副组长、中国医促会泌尿外科分会副主任委员、中国医师协会泌尿外科肿瘤委员会委员、中国研究型医院学会罕见病分会常务理事、国际 VHL 联盟咨询委员(中国唯一)、《中国泌尿外科疾病诊断治疗指南——前列腺癌》编委。
1. Xie, H., Zhou, J., Liu, X., Xu, Y., Hepperla, J. A., ... & Gong, K.*, Zhang, Q.* (2022). USP13 promotes deubiquitination of ZHX2 and tumorigenesis in kidney cancer. PNAS, 119(36): e2119854119. (IF=11.1)
2. Zhou, J., & Gong, K.* (2022). Belzutifan: a novel therapy for von Hippel–Lindau disease. Nature Reviews Nephrology, 1-2. (IF= 42.439)
3. Hu, L., Xie, H., Liu, X., Potjewyd, F., James, L. I., Wilkerson, E. M., ... & Gong, K.*, Zhang, Q.* (2019). TBK1 is a Synthetic Lethal Target in Cancer with VHL Loss. Cancer Discovery, 10(3): 460-475. (IF= 38.272)
4. Ning, X. H., Zhang, N., Li, T., Wu, P. J., Wang, X., Li, X. Y., ... & Gong, K.* (2014). Telomere shortening is associated with genetic anticipation in Chinese Von Hippel–Lindau disease families. Cancer research, 74(14), 3802-3809. (IF= 13.312)
5. Liu, S. J., Wang, J. Y., Peng, S. H., Li, T., Ning, X. H., Hong, B. A., ... & Gong, K.* (2018). Genotype and phenotype correlation in von Hippel–Lindau disease based on alteration of the HIF-α binding site in VHL protein. Genetics in Medicine, 20(10), 1266. (IF= 8.864)
2017年 “国家高层次人才特殊支持计划(中组部万人计划)”
2016年 科技部“中青年科技创新领军人才”
2015年 中华医学科技奖三等奖(第一完成人)
2014年 北京大学医学部优秀党员
2012年 教育部科技进步二等奖(第一完成人)
2011年 华夏科技进步奖二等奖(第一完成人)
2010年 教育部“新世纪优秀人才”








 北京市西城区西什库大街8号
北京市西城区西什库大街8号 100034
100034 83572211
83572211